Table of Contents
UN ESCAP Definition of Good Governance
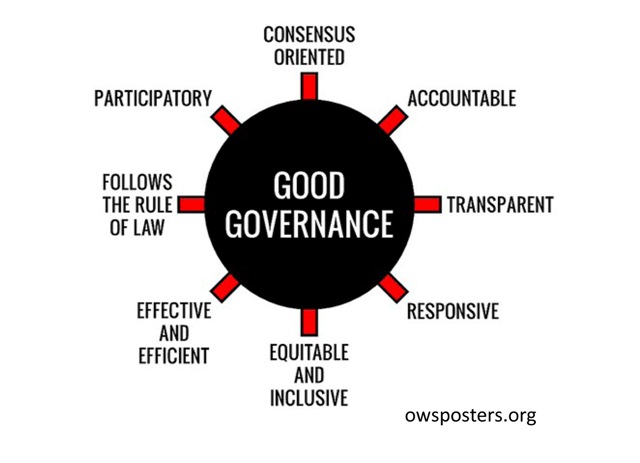
Good governance has 8 major characteristics. It is participatory, consensus oriented, accountable, transparent, responsive, effective and efficient, equitable and inclusive and follows the rule of law. It assures that corruption is minimized, the views of minorities are taken into account and that the voices of the most vulnerable in society are heard in decision-making. It is also responsive to the present and future needs of society.
Features of Good Governance
- Participatory
- Consensus oriented
- Responsive
- Transparent
- Accountable
- Effective and Efficient
- Equitable and Inclusive
- Follow Rule of Law
For detailed explanation of the above terms, you can refer to the following short document.
4 Pillars of Good Governance
- Ethos: of service to citizens
- Ethics: honesty, integrity and transparency
- Equity: treating all citizens equally with sympathy for weaker sections
- Efficiency: fast and effective service delivery without harassment, use of ICT
Citizen’s Charter
Instrument to make an organization citizen friendly, transparent and accountable. Read more about Citizen’s Charter
7 Principles of Citizen Centricity
- Define the public services available and identify the clients
- Set standards and norms of service delivery
- Develop capabilities to deliver the standards
- Perform to achieve the standards
- Monitor performance against the standards
- Independent evaluation
- Improvement based upon the evaluation
6 Principles of Citizen’s Charter
- Quality: Improving quality of service
- Choice: Provide choices wherever available
- Value for money for taxpayers
- Accountability: both individual and organizational
- Transparency: in rules, procedures and grievance redressal
- Standards: specifying what to expect within a timeframe
Steps to Improve Good Governance
- Citizen Centricity
- Social Audit
- Participation (suggestions and feedback)
- Women’s participation
- Decentralization (political, fiscal, administrative)
- Effective delegation of duties (Principle of subsidiarity)
- Inclusivity or accessibility to the differently abled
- Grievance Redressal
- CVC, National Commission for SC, NCST, Lokpal, National Commission for Protection of Child Rights, Consumer Courts
- Use of technology
- Simplifying processes
- e.g. simplifying attestation processes, single window clearance)
- e.g. Jaankari Project of Bihar govt. to make RTI queries through phone call
- Periodic Monitoring and Evaluation
- Robust enforcement institutions and mechanisms
Great Initiative Sir. Thank you 🙂