In this lesson we discuss India Bangladesh relations from UPSC Preparation point of view. Major highlights of Indo-Bangla relations will be discussed here including recent developments in India Bangladesh relations.
READ PREVIOUS LESSON: India’s Neighbourhood Policy
READ FIRST LESSON: Principles of Indian Foreign Policy
Table of Contents
Why Bangladesh is Important for India?
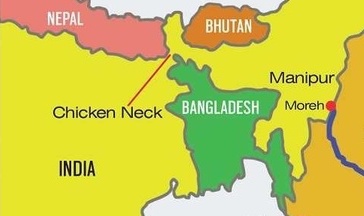
- It divides mainland India from the North-East India. Support of Bangladesh is required for economic integration of North-East.
- It also creates ‘chicken-neck’ near Siliguri. Thus it is important from security point of view to engage with Bangladesh
- Bangladesh is a backyard for terrorist networks and insurgency activities. Earlier, during Khaleda Zia’s rule (Bangladesh Nationalist Party), both these activities had increased. Insurgents would carry out operations in Indian territory and re-enter Bangladesh for shelter.
- Bangladesh can provide access to sea to the North-East states and help promote commerce and economy.
- In the Act East policy of India, Bangladesh is an indispensable part.
- Indo-Bangladesh border is long and porous, specially because of many rivers. Thus human/animal trafficking is rampant.
- Good relations with Bangladesh earns us goodwill of Islamic nations.
- Bangladesh is one of the fastest growing economies in the world.
- Refugee crisis and illegal immigrant issues.
- Water disputes, e.g. Farakka Barrage issue, Teesta Water Sharing Agreement etc.
Issues between India and Bangladesh
Following are the contentious issues between India and Bangladesh in their relation:
Land Boundary Issues
India and Bangladesh both had enclaves in each other’s territory. Enclaves are the territories of a country which are completely surrounded by territory of another country. The two countries even had second and third degree enclaves! It means that there was enclave within an enclave within an enclave.
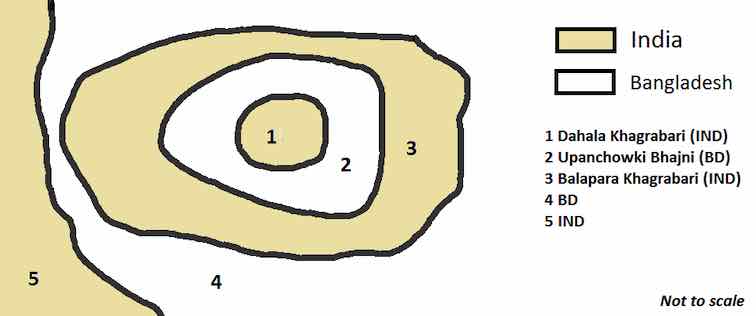
This issue was created because the boundary was decided hurriedly on paper and not on the ground. However, the issue was resolved via 2015 India-Bangladesh Land Boundary Agreement. It was signed in 1972 but ratified in 2015. India transferred 111 enclaves to Bangladesh while received 51 enclaves in return. This agreement was validated by the 100th Constitutional Amendment Act.
Water Sharing Issues between India and Bangladesh
India is upper riparian while Bangladesh is lower riparian. It means that rivers flow through India first and then enter Bangladesh. There are about 54 such transboundary rivers. This is why Bangladesh remains anxious about water security through rivers.
Farakka Barrage Issue
It was built upon Ganges river in Murshidabad district of West Bengal in 1975. The purpose was to divert water to Bhagirathi-Hoogly river system. The river enters Bangladesh after it and they say that they do not get enough water. That region is also the most densely populated river basin in the world.
India uses the diverted water to ensure proper functioning of Kolkata Port and running of NTPC plant in Farakka. India is also facing at water-stress by 2025 and water-scarcity by 2050. Thus greater sharing more water with Bangladesh becomes unfeasible. Read more about the issue here.
Ganges Water Sharing Treaty
It is also called the Ganges Water Treaty. It was signed in 1996 to decide the Ganges water sharing formula. Bangladesh Nationalist Party (BNP) is against this treaty. They accuse India of not giving sufficient water.
Teesta Water Dispute
Teesta originates in Sikkim. It flows through some of the poorest regions in India and Bangladesh. Countless fishermen, farmers and boatman depend on the river flow on both sides. Due to dam construction on Indian side, the flow has reduced in Bangladesh, particularly in the dry season. There is no treaty to direct the water sharing formula.
It is also a politically sensitive issue for both West Bengal and Bangladesh. In 1984, the issue was referred to Indo-Bangladesh Joint River Commission (JRC). The JRC reasonably awarded more water to Bangladesh but West Bengal protested. Since water is a state subject, the JRC recommendation was not implemented.
Issue of Illegal Migrants from Bangladesh
After creation of Pakistan, a large number of Hindus from Bangladesh fled to India. The immigration increased drastically when many sought refuge in India during 1971 war. Even many non-Hindu immigrants enter and settle in India illegally almost everyday, particularly in Assam and West Bengal.
This has created local political issues. The current government initiated NRC in Assam and also talked about implementing NRC in West Bengal. There were rhetorics against illegal Bangladeshis in India. This created discord between the two countries.
Recent Developments in Indo-Bangla Reations
In the recent diplomatic engagement, India and Bangladesh signed many treaties, including:
- India will set up coal power plants in Bangladesh. They will be connected to India’s power grid. India will give 100 MW power in exchange of 10Gbps internet bandwidth to North East.
- L&T and Adani will invest in Bangladesh’s power sector.
- Total volume of trade between India and Bangladesh is $7 billion. But Bangladesh has huge trade deficit.To reduce the trade deficit, India would consider decreasing tariff barriers and promote border haats.
So this lesson was about India Bangladesh Relations. In the next Lesson, we shall learn about India-Nepal Relations.